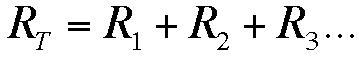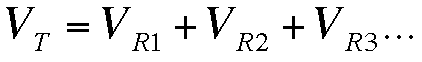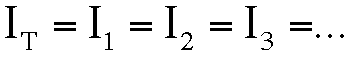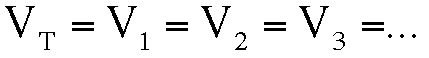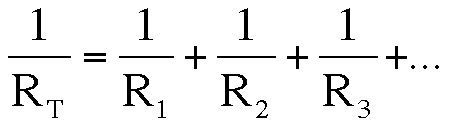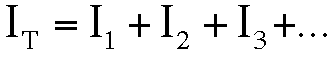ELECTRICITY &
ELECTRONICS
Immerse yourself in the world of technology in the most entertaining way.
Types of circuits- Tipos de circuitos
-Series circuits: in series circuit receptors are installed next to each other in the power line, so that the current flowing through the first one is the same as that one flowing the last.
The total resistance of the circuit is the addition of each of the resistances that composes the circuit:
The voltage of several generators in series is:
The current is always the same:
Example of a series circuit:
-Parallel circuits: each receptor connected to power source it is independently connected from the rest.
The potential difference is always the same but the current flowing through each branch is different:
The total current is the sum of the current in the different branches:
The equivalent resistance is the following:
Example of parallel circuit:
-Mixed circuits: in mixed circuits some elements are connected in paraller and others in series.
They mantain the current of the elements in series and the voltage of the ones in parallel.
If we want to calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit we just have to calculate the partial resistance of each branch and combine.
Example of mixed circuit: